Introduction
Architectures is more than just buildings it is an expression of culture, technology and human ingenuity. From ancient temples to futuristic skyscrapers, architecture shapes our lives and societies. But how has architectures evolved ? What are the key principles that define great design? And where is the future of architecture headed? This guide will answer all these questions and more.
Let’s embark on a journey through the fascinating world of architectures, exploring its history, styles, and modern advancements.
The Evolution of Architectures
Architecture has evolved over thousands of years, influenced by cultural, technological and environmental factors.
Ancient Architectures (Prehistoric – 500 CE)
- The Pyramids of Egypt (c. 2600 BCE) symbolize early engineering mastery.
- The Greek Parthenon showcases classical symmetry and proportion.
- Roman innovations like the Colosseum introduced advanced construction techniques.
Medieval Architectures (500 – 1400 CE)
- Gothic cathedrals such as Notre Dame featured pointed arches and stained glass.
- Islamic architecture, like the Alhambra, emphasized intricate tilework.
Renaissance and Baroque Architectures (1400 – 1750 CE)
- Renaissance architects revived classical elements with a focus on harmony and realism.
- Baroque designs introduced grandeur, with dramatic contrasts in light and space.
Neoclassical and Modern Architectures (1750 – Present)
- The 19th century saw the rise of Neoclassicism and industrial materials.
- The 20th and 21st centuries brought skyscrapers, sustainable design and digital innovation.
Key Architectural Styles
| Style | Period | Characteristics | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classical | Ancient Greece & Rome | Symmetry, columns, proportionality | Parthenon, Rome’s Pantheon |
| Gothic | 12th–16th century | Pointed arches, ribbed vaults, flying buttresses | Notre Dame Cathedral |
| Renaissance | 14th–17th century | Revival of classical styles, domes | Florence Cathedral |
| Baroque | 17th–18th century | Dramatic use of light, grandeur | Palace of Versailles |
| Modern | 20th century–Present | Minimalist, functional, glass and steel | The Guggenheim, Fallingwater |
| Sustainable | 21st century | Eco-friendly materials, green roofs | The Edge (Amsterdam) |
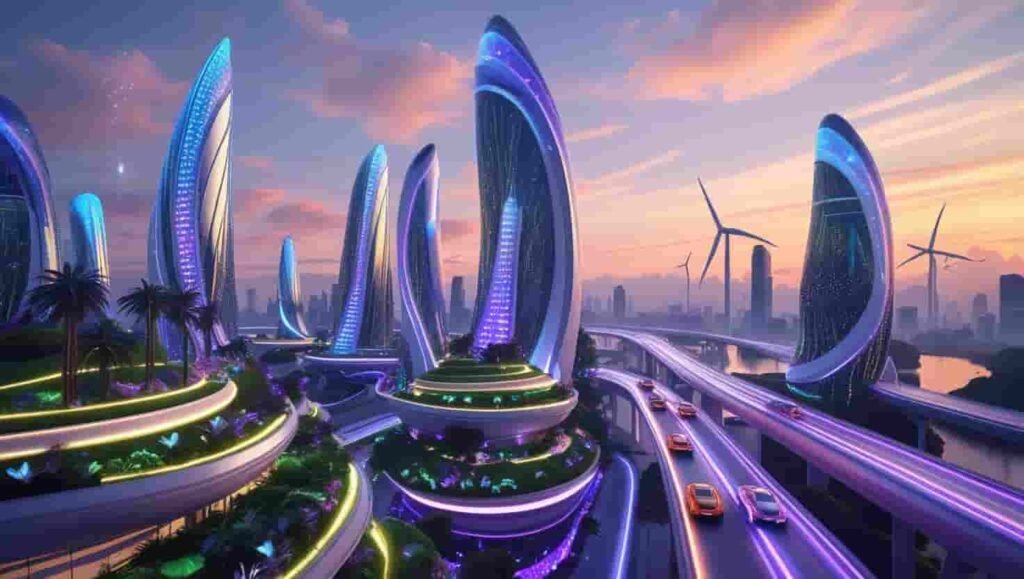

Fundamental Principles of Architectures
Great architecture follows a set of principles that balance aesthetics, function, and sustainability.
- Balance & Proportion: The relationship between different elements.
- Functionality: Buildings must serve their intended purpose efficiently.
- Sustainability: Eco-conscious design reduces environmental impact.
- Innovation: Use of new materials and techniques.
Elements of Architectural Design
- Space: How areas are arranged and utilized.
- Light & Shadow: Natural and artificial lighting impact mood.
- Materials: Wood, glass, concrete, steel each has distinct properties.
- Structure: Load-bearing elements that support a building.
Influence of Technology on Modern Architectures
Modern architecture has been revolutionized by technology:
- 3D Printing allows for rapid prototyping of complex structures.
- AI & Smart Homes enhance user experience with automation.
- Virtual Reality (VR) helps architects visualize projects before construction.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Architecture
Green architecture aims to minimize environmental impact by reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable building practices.
- Solar Panels & Wind Turbines for energy efficiency.
- Green Roofs & Living Walls for better insulation.
- Recyclable Materials to minimize waste.
Famous Architects and Their Masterpieces
- Frank Lloyd Wright – Fallingwater (USA)
- Zaha Hadid – Heydar Aliyev Center (Azerbaijan)
- Le Corbusier – Villa Savoye (France)
Role of Architecture in Urban Development
Architecture plays a vital role in shaping cities by improving:
- Infrastructure
- Housing quality
- Public spaces
Smart city concepts integrate sustainable and digital technologies for better living environments.
Table: A Comparison of Architectural Styles
| Feature | Classical | Gothic | Renaissance | Modern |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Marble, stone | Stone, glass | Brick, plaster | Concrete, steel |
| Structure | Symmetrical | Vertical emphasis | Proportional harmony | Minimalist, geometric |
| Key Example | Parthenon | Notre Dame | St. Peter’s Basilica | The Shard |
FAQs
Q2: How does technology impact architecture today?
Modern architecture benefits from AI, VR, and sustainable innovations for better efficiency and design.
Q3: What are the most famous buildings in the world?
Iconic buildings include the Eiffel Tower, Burj Khalifa, Sydney Opera House, and Taj Mahal.
Q4: What makes a building sustainable?
A sustainable building uses eco-friendly materials, renewable energy sources and smart water management.
Conclusion
Architecture is a powerful discipline that blends creativity, science and culture. From ancient temples to futuristic eco-homes, it continues to shape human civilization. The future of architecture is sustainable, technology-driven and highly innovative. As cities grow, architecture will play an even more crucial role in creating efficient, eco friendly and aesthetically pleasing spaces.



Pingback: Arts
Pingback: Roman Arts | Ancient Roman Art | Roman Art
Pingback: District and Session Judge, Mirpurkhas Jobs 2024 Online Apply
Pingback: Egyptian Arts | Art of ancient Egypt | Ancient Egyptian Art