Introduction
Chinese arts represent one of humanity’s oldest and most continuous artistic traditions spanning over 5000 years of cultural evolution From the ethereal brush strokes of landscape paintings to the precise movements of traditional dance Chinese artistic expression embodies a profound philosophy that unites humanity with nature This rich artistic heritage has not only shaped East Asian culture but continues to influence global artistic movements today Through a deep exploration of various art forms from classical calligraphy to contemporary installations we uncover how Chinese arts maintain their relevance while honoring ancient traditions
The Foundational Arts
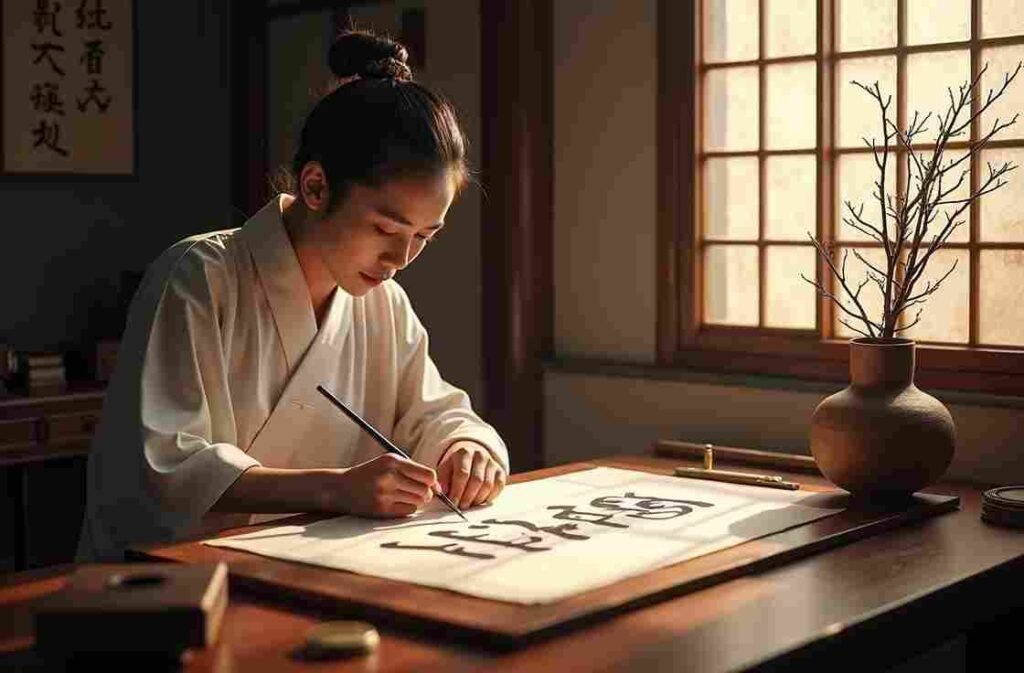
Calligraphy The Supreme Art Form
Chinese calligraphy stands as perhaps the most revered of all traditional art forms considered equal to or even superior to painting in classical Chinese culture
Historical Development
The evolution of Chinese calligraphy encompasses
- Oracle bone inscriptions jiaguwen from the Shang Dynasty
- Bronze inscriptions of the Zhou period
- Development of various script styles through the dynasties
- Modern interpretations and experimental forms
Major Scripts and Styles
Traditional calligraphy includes five major script types
- Seal Script 篆书 The oldest standardized style
- Clerical Script 隶书 Developed during the Han Dynasty
- Regular Script 楷书 The standard script used today
- Running Script 行书 A semi cursive form
- Cursive Script 草书 The most fluid and abstract style
Traditional Painting
The Three Perfections
Chinese painting traditionally integrates
- Calligraphy
- Poetry
- Painting itself
This unity creates works that engage multiple senses and artistic disciplines
Dominant Genres
Traditional Chinese painting focuses on several key subjects
- Landscape painting 山水画
- Bird and flower painting 花鸟画
- Figure painting 人物画
- Animal painting 动物画
Techniques and Materials
Traditional painters utilize
- Ink and brush techniques
- Special papers and silks
- Mineral and vegetable pigments
- Specific brush types for different effects

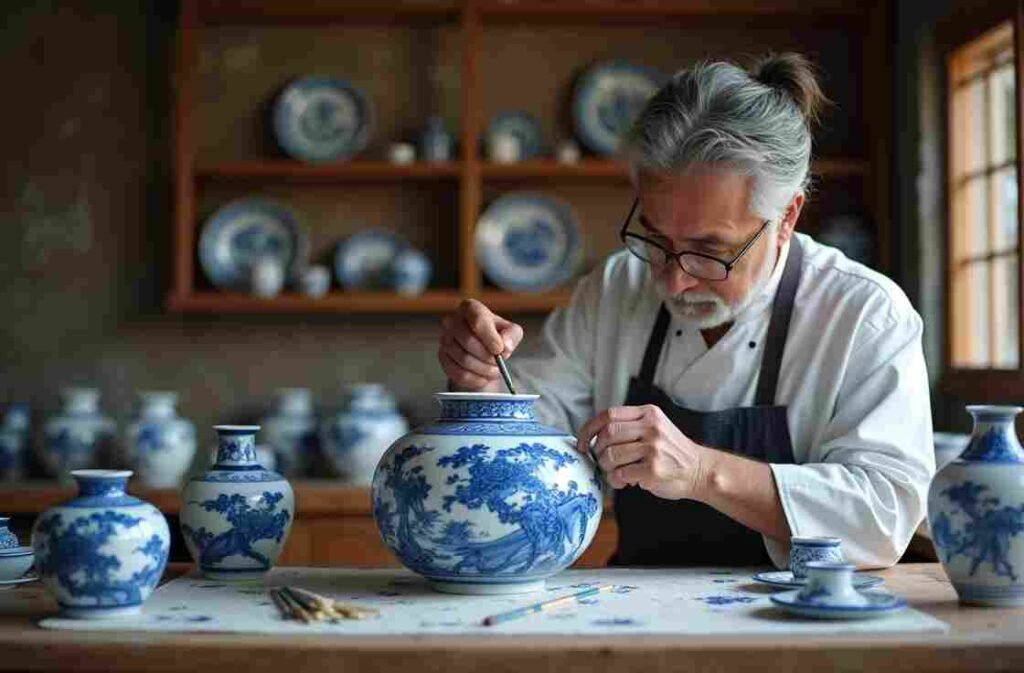
Ceramic Arts and Pottery
Historical Development
Early Pottery
The evolution of Chinese ceramics includes
- Neolithic painted pottery
- Proto porcelain development
- Early glazing techniques
- Regional variations in style and technique
Porcelain Innovation
China’s contribution to global ceramic arts includes
- Development of true porcelain
- Blue and white pottery techniques
- Multiple firing methods
- Glazing innovations
Major Types and Styles
Famous Varieties
Notable Chinese ceramics include
- Jingdezhen porcelain
- Celadon ware
- Jun ware
- Yixing pottery
Traditional Performance Arts
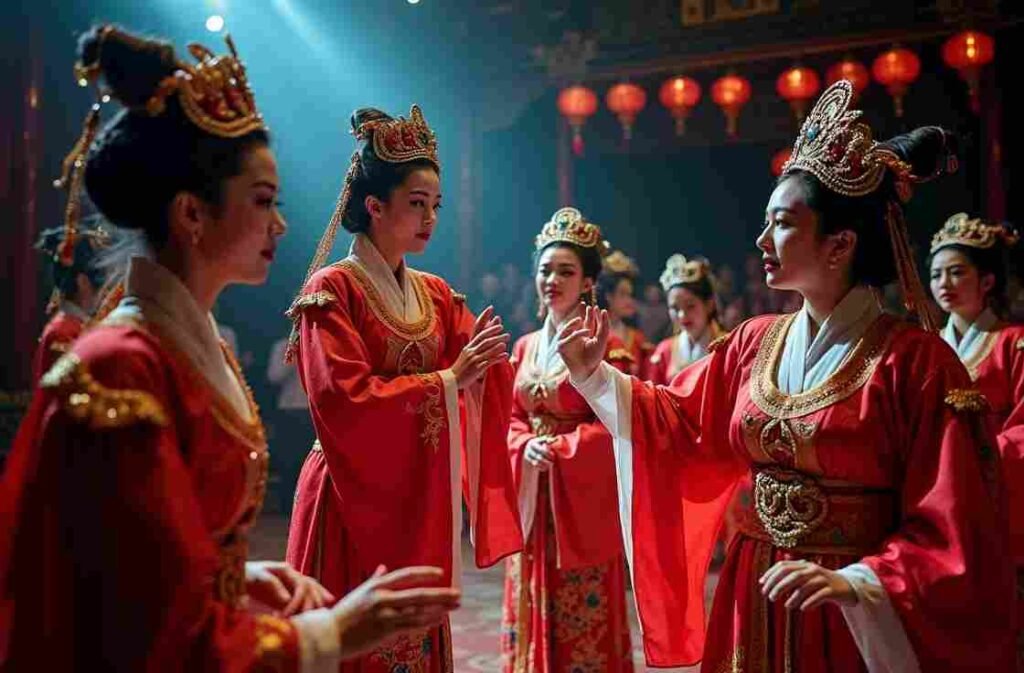
Chinese Opera
Regional Styles
Major operatic traditions include
- Peking Opera
- Kunqu Opera
- Cantonese Opera
- Sichuan Opera
Elements of Performance
Traditional opera combines
- Elaborate costumes and makeup
- Stylized movement and gesture
- Complex musical accompaniment
- Symbolic stage properties


Traditional Music
Instruments and Composition
Classical Chinese music features
- The eight tone classification system
- Pentatonic scale basis
- Traditional instruments like guqin and pipa
- Regional instrumental traditions
Architectural Arts
Traditional Architecture
Principles and Philosophy
Chinese architecture embodies
- Harmony with nature
- Feng shui principles
- Hierarchical organization
- Symbolic decoration
Major Features
Characteristic elements include
- Dougong bracket systems
- Upturned eaves
- Courtyard layouts
- Color symbolism
Contemporary Chinese Arts
Modern Innovations
Current Trends
Contemporary Chinese art explores
- Digital media and installation art
- Environmental themes
- Cultural identity questions
- Global art market engagement
Notable Movements
Recent developments include
- Political Pop
- Cynical Realism
- New Media Art
- Experimental Ink Painting
Preservation and Future Directions
Conservation Efforts
Current initiatives focus on
- Digital documentation
- Traditional crafts preservation
- Educational programs
- International collaboration
Innovation in Traditional Arts
Modern approaches include
- Digital calligraphy tools
- Virtual reality exhibitions
- Cross cultural fusion
- Sustainable art practices

Frequently Asked Questions
Q How has Chinese art influenced global culture
Chinese artistic innovations have profoundly influenced global culture particularly in ceramics ink painting and architectural design Chinese aesthetic principles continue to inspire contemporary artists worldwide
Q What materials are traditionally used in Chinese painting
Traditional Chinese painting primarily uses ink brushes made from animal hair rice paper or silk and mineral or vegetable pigments The Four Treasures of the Study brush ink paper and inkstone are essential tools
Q How is traditional Chinese art being preserved
Preservation efforts include government support for master artists digital documentation of techniques educational programs and the establishment of cultural heritage sites and museums
Q What role does symbolism play in Chinese art
Symbolism is central to Chinese art with specific colors animals plants and patterns carrying deep cultural meanings These symbols often convey wishes for prosperity longevity and harmony
Q How has modernization affected traditional Chinese arts
Modernization has brought both challenges and opportunities leading to new artistic expressions while sometimes threatening traditional practices Many artists now blend traditional techniques with contemporary themes
Q What distinguishes Chinese calligraphy from other writing systems
Chinese calligraphy is unique in its emphasis on artistic expression through brush strokes its integration with painting and poetry and its status as a fine art form rather than mere writing
Q How can beginners start learning Chinese art
Beginners can start through formal classes online tutorials workshops or by studying basic calligraphy Understanding the philosophical principles behind Chinese art is also important
Q What role do traditional arts play in modern Chinese society
Traditional arts remain important in modern Chinese society serving as cultural symbols sources of national pride and bridges between generations
Q How is technology changing Chinese arts
Technology is transforming how Chinese arts are created preserved and shared with digital tools enabling new forms of expression while helping document traditional techniques
Conclusion
The journey through Chinese arts reveals a profound cultural heritage that continues to evolve and inspire From ancient calligraphy to contemporary digital art Chinese artistic expression maintains its vitality while honoring traditional principles As we look to the future the challenge lies in preserving these invaluable traditions while embracing new forms of creative expression