Introduction
The Gupta period (320-550 CE) marks what historians often call the “Golden Age” of Indian art and architecture. During this remarkable era artistic expression reached unprecedented heights of sophistication establishing standards that would influence South Asian aesthetics for centuries to come. Under the patronage of powerful Gupta rulers artists and architects created works that perfectly balanced indigenous traditions with innovative techniques resulting in a distinctive style that epitomized classical Indian art. This period witnessed the construction of magnificent temples the creation of exquisite sculptures and the development of sophisticated painting techniques that continue to captivate audiences worldwide.
The Historical Context of Gupta Art and Architecture
Political Climate and Cultural Renaissance
The Gupta Empire emerged as a unified force in the 4th century CE bringing political stability and economic prosperity to large parts of the Indian subcontinent. This period of peace and abundance created ideal conditions for artistic and architectural development supported by:
- Royal patronage from enlightened rulers
- Thriving trade networks that facilitated cultural exchange
- Agricultural surplus that funded massive building projects
- A sophisticated urban culture that demanded artistic expression
Religious Influences
The Gupta period saw the harmonious coexistence of multiple religious traditions each contributing to the artistic landscape:
- Hinduism experienced a significant revival
- Buddhism continued to flourish
- Jainism maintained its distinctive artistic traditions
- Various indigenous beliefs influenced artistic expression
Architectural Achievements
Temple Architecture
The Gupta period revolutionized Hindu temple architecture establishing patterns that would influence Indian sacred architecture for centuries.
Key Innovations in Temple Design
The period introduced several architectural innovations:
- The emergence of the Nagara style in North India
- Development of the shikhara (temple spire)
- Integration of mandapa (pillared hall) with the main shrine
- Standardization of the temple ground plan
Notable Temple Examples
Dashavatara Temple at Deogarh
This temple represents one of the earliest examples of the classical Gupta style. Its features include:
- Sophisticated sculptural reliefs
- Complex architectural planning
- Integration of multiple shrine chambers
- Advanced structural engineering techniques
Vishnu Temple at Tigawa
Notable for its:
- Simple yet elegant design
- Early example of the Nagara style
- Well-preserved architectural elements
- Innovative use of space and light
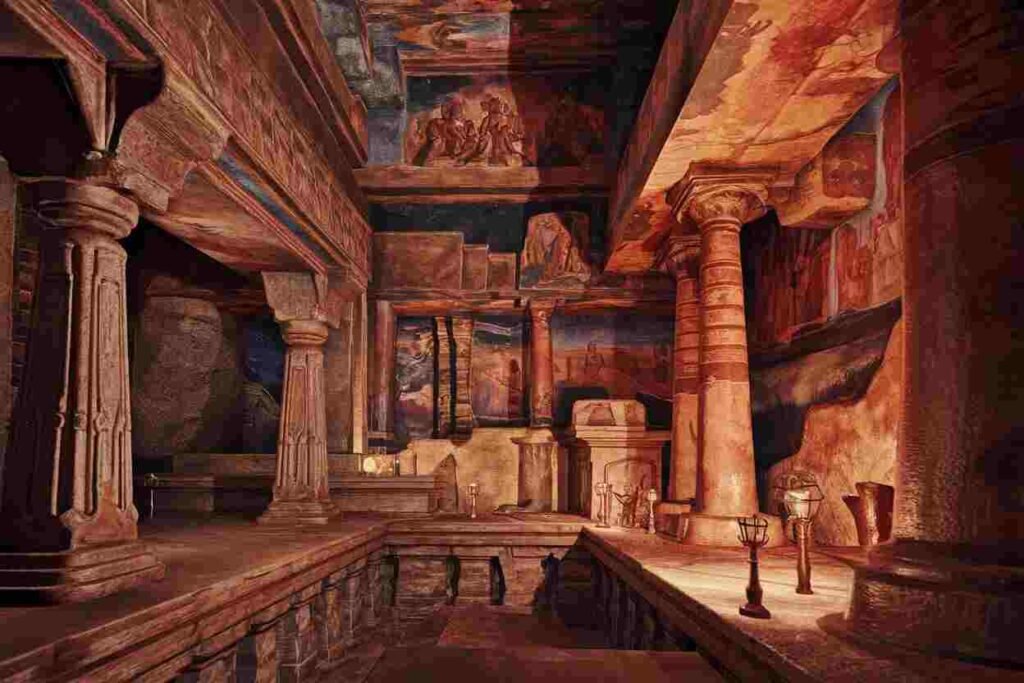
Cave Architecture
The Gupta period saw significant developments in cave architecture particularly evident in:
Ajanta Caves
These caves showcase:
- Advanced architectural planning
- Sophisticated water management systems
- Integration of painting and sculpture
- Complex spatial organization
Udayagiri Caves
Notable features include:
- Refined rock-cut architecture
- Innovative sculptural programs
- Integration with natural landscape
- Advanced engineering solutions
Sculptural Arts
Religious Sculpture
The Gupta period represents the pinnacle of Indian sculptural art characterized by:
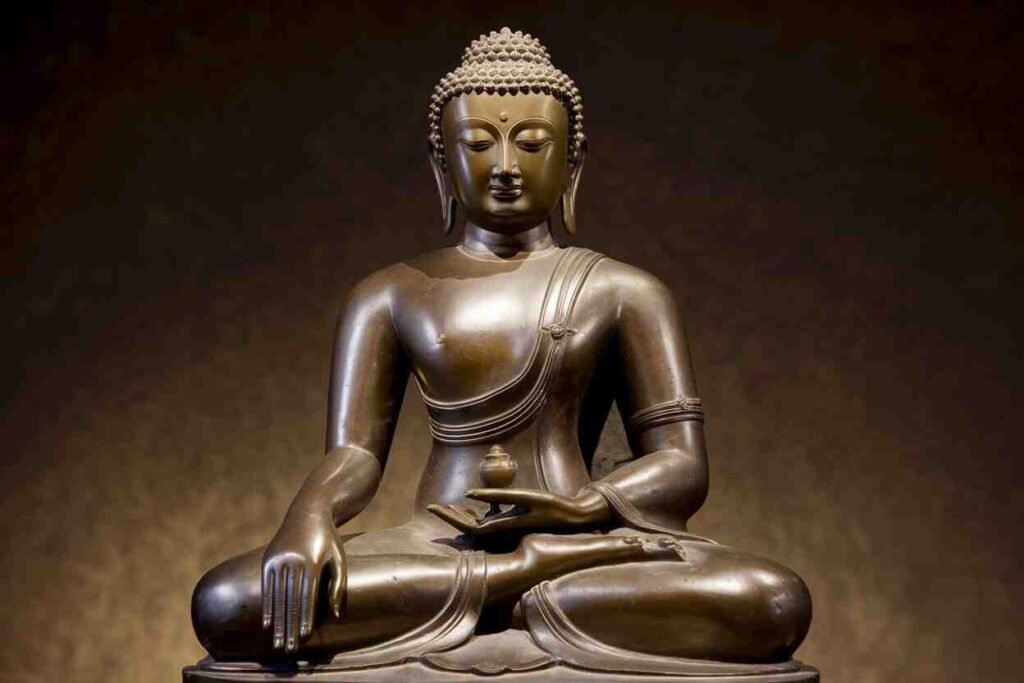
Buddhist Sculpture
- Refined portrayal of the Buddha
- Sophisticated modeling techniques
- Spiritual expression through form
- Integration of Greek influences
Hindu Sculpture
- Development of iconic forms
- Standardization of deity representation
- Advanced anatomical understanding
- Expression of rasa (aesthetic emotion)
Secular Sculpture
While religious themes dominated secular sculpture also flourished:
- Portrait sculptures of rulers
- Decorative architectural elements
- Genre scenes from daily life
- Animal and nature studies

Painting Traditions
Ajanta Cave Paintings
The magnificent murals at Ajanta represent the height of Gupta painting.
Technical Achievements
- Advanced use of perspective
- Sophisticated color preparation
- Innovative painting techniques
- Durability of materials
Thematic Content
- Buddhist narratives
- Court scenes
- Natural landscapes
- Daily life depictions
Manuscript Illustration
The Gupta period saw the development of:
- Palm leaf manuscript illustration
- Religious text decoration
- Scientific manuscript illustration
- Narrative painting techniques
Decorative Arts
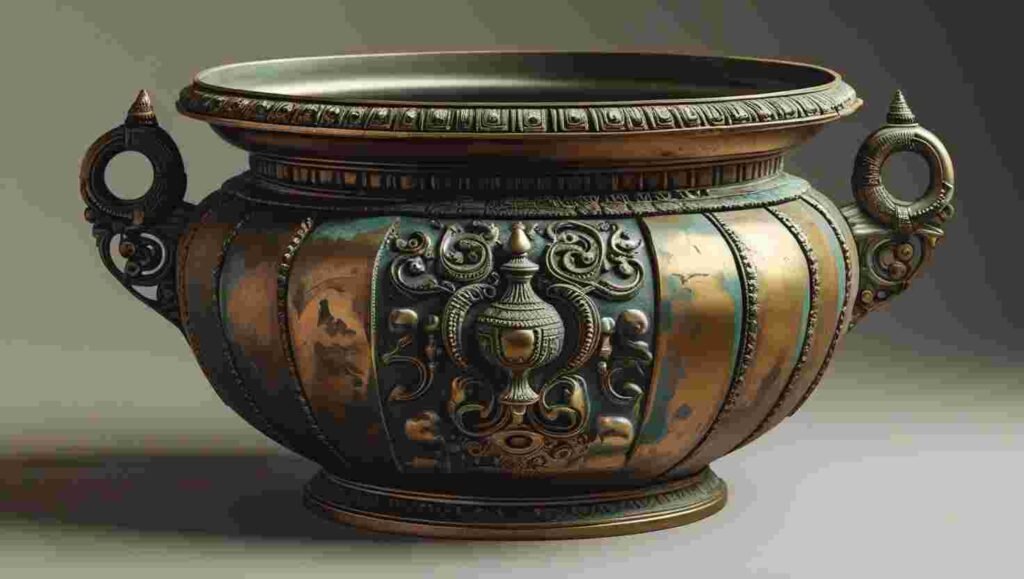
Metal Work
The period excelled in:
- Bronze casting
- Gold and silver work
- Copper alloy crafting
- Decorative metalware
Terracotta Art
Notable developments include:
- Sophisticated modeling techniques
- Mass production methods
- Integration of local styles
- Advanced firing techniques

Technical Innovations
Building Technology
The period introduced:
- Advanced stone-cutting techniques
- Innovative joining methods
- Structural engineering solutions
- Water management systems
Material Science
Developments included:
- New mortar compositions
- Metal working techniques
- Paint preparation methods
- Stone selection criteria

Cultural Impact and Legacy
Influence on Later Art
The Gupta period established:
- Artistic standards for centuries
- Iconographic conventions
- Technical benchmarks
- Aesthetic principles
Global Recognition
The period’s achievements are acknowledged through:
- UNESCO World Heritage sites
- International exhibitions
- Academic research
- Cultural preservation efforts
Modern Relevance
Contemporary Applications
The Gupta artistic tradition influences:
- Modern temple architecture
- Contemporary Indian art
- Conservation techniques
- Cultural identity
Conservation Efforts
Current initiatives focus on:
- Scientific preservation
- Digital documentation
- Public awareness
- Research and study
FAQ
Q2. How did religious diversity influence Gupta art and architecture?
The period's religious diversity led to a rich artistic synthesis. Buddhist Hindu and Jain traditions contributed unique elements to the artistic vocabulary resulting in a sophisticated visual language that transcended individual religious boundaries.
Q3. What are the key characteristics of Gupta temple architecture?
Gupta temples are characterized by their refined proportions sophisticated planning integration of sculptural elements and the development of the Nagara style. Key features include the shikhara (spire) mandapa (pillared hall) and standardized ground plans.
Q4. How did Gupta period sculptures influence later Indian art?
Gupta sculpture established canonical forms for deity representation perfected techniques for expressing emotion and movement and created standards for proportions and composition that influenced Indian art for over a millennium.
Q5. What techniques were used in Gupta period paintings?
Gupta artists developed sophisticated techniques for preparing pigments creating perspective and executing murals. They used natural materials and advanced binding methods to create durable works as seen in the Ajanta cave paintings.
Q6. How did trade and economy impact Gupta period art?
Prosperous trade networks and strong economic conditions enabled royal patronage of arts facilitated material acquisition and allowed for cultural exchange that enriched artistic traditions.
Q7. What role did mathematics and science play in Gupta architecture?
Advanced mathematical knowledge enabled precise architectural planning while scientific understanding of materials and engineering principles allowed for innovative structural solutions.
Q8. How are Gupta period artistic traditions preserved today?
Modern conservation efforts combine traditional knowledge with scientific techniques. Digital documentation research programs and public awareness campaigns help preserve this artistic heritage.
Conclusion
The art and architecture of the Gupta period represent one of humanity’s greatest artistic achievements. The period’s innovations in temple architecture sculpture painting and decorative arts established standards that influenced Indian art for over a millennium. As we continue to study and preserve these magnificent works we ensure that future generations can learn from and be inspired by this remarkable artistic heritage.
The Gupta artistic legacy remains relevant today informing contemporary architectural practices conservation efforts and cultural identity. As we face modern challenges in preserving and interpreting this heritage the sophisticated solutions developed during the Gupta period offer valuable insights and inspiration.
Understanding and appreciating Gupta period art and architecture isn’t just an academic exercise—it’s crucial for understanding the development of Indian civilization and its contributions to world culture. As we continue to study and preserve these magnificent works we ensure that future generations can learn from and be inspired by this remarkable artistic heritage.