Journalism plays a crucial role in shaping societies, influencing public opinion and holding those in power accountable. It is a profession that revolves around collecting, verifying, analyzing and presenting news to the public. Over the years, journalisms has evolved significantly with the advent of digital media, social networks and artificial intelligence.
This article delves deep into the world of journalisms, covering its history, types, ethics, challenges and the impact it has on democracy and society. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of journalism and its significance in our daily lives.
Introduction to Journalism
Journalism is the process of obtaining, analyzing, producing and presenting news and information. It serves as the eyes and ears of the public, helping people stay informed about local, national and global events. A journalist’s duty is not only to report facts but also to ensure that the information shared is accurate, unbiased and impactful.

Definition of Journalism
“Journalism is the production and distribution of reports on current events based on facts and supported with proof or evidence.”
It involves various mediums such as print (newspapers, magazines), broadcast (radio, television) and digital (websites, social media).
History and Evolution of Journalism
Early Journalism (Before the Printing Press)
- The earliest form of journalisms dates back to Ancient Rome, where public notices were inscribed on stone tablets.
- In China, news was distributed through government bulletins called “Dibao” during the Han Dynasty.
The Printing Press Era (15th–18th Century)
- Johannes Gutenberg invented the printing press in the 15th century which changed journalisms.
- The first newspaper, Relation, was produced in Germany in 1605.
- By the 18th century, newspapers were widely available in Europe and America.
The Rise of Modern Journalism (19th–20th Century)
- The 19th century saw the rise of investigative journalisms and the emergence of press agencies like Reuters and Associated Press.
- Radio and television journalisms took over in the 20th century, making news more accessible.
The Digital Age (21st Century – Present)
- The internet has drastically changed journalisms, allowing for instant news reporting through websites, blogs and social media.
- AI and big data are now being used to analyze news trends and predict future events.
Types of Journalism
| Type of Journalism | Description |
|---|---|
| Investigative journalisms | Deep research to uncover hidden truths |
| Political journalisms | Focuses on government policies and political events |
| Business journalisms | Covers financial markets, companies, and the economy |
| Sports journalisms | Reports on sports events, athletes, and competitions |
| Entertainment journalisms | Covers movies, celebrities, and cultural events |
| Science journalisms | Focuses on technological and scientific advancements |
| Environmental journalisms | Reports on climate change, conservation, and nature |
| War journalisms | Covers conflicts and wars from the battlefield |
Each type of journalisms serves a unique purpose and requires specific skills and knowledge.
Role and Importance of Journalism
A democratic society relies heavily on journalism. Here’s why it matters:
- Informs the Public: journalisms keeps people updated on current events and trends.
- Holds Power Accountable: Investigative journalisms exposes corruption and unethical practices.
- Gives a Voice to the Voiceless: Journalists highlight social injustices and unheard stories.
- Promotes Transparency: A free press ensures that governments and businesses remain transparent.
- Encourages Civic Engagement: Informed citizens are more likely to participate in democratic processes like voting.
Ethics and Principles in Journalism
A journalist must adhere to a strict code of ethics to maintain credibility. The key principles include:
- Truth and Accuracy: Reporting must be fact-based and verified.
- Independence: Journalists should remain free from political or commercial influence.
- Fairness and Impartiality: News should present balanced perspectives.
- Humanity: Avoid causing unnecessary harm to individuals or communities.
- Accountability: Journalists must correct errors and take responsibility for their reports.
Challenges Faced by Journalists
- Fake News & Misinformation: The spread of false information has become a major problem.
- Censorship & Press Freedom: Some governments suppress journalisms to control narratives.
- Safety & Security Risks: Journalists in war zones and authoritarian states face threats.
- Economic Struggles: Traditional media faces financial decline due to digital competition.
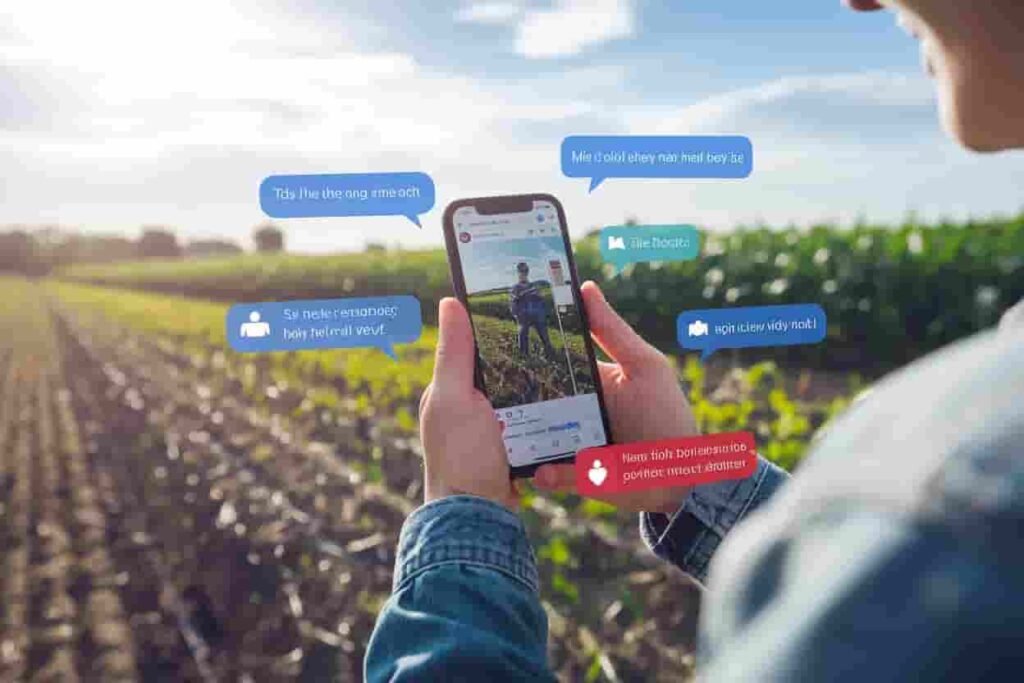
The Digital Revolution and Its Impact on Journalism
- Social media platforms have emerged as key news providers.
- AI-powered news aggregation is changing how stories are curated.
- Subscription-based journalisms is replacing ad-driven models.
Investigative Journalism: Exposing the Truth
Investigative journalists like Bob Woodward and Carl Bernstein exposed the Watergate scandal, proving how journalism can change history.
Journalism vs. Propaganda : Understanding the Difference
| Aspect | Journalism | Propaganda |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Report facts | Influence opinions |
| Bias | Minimally biased | Highly biased |
| Source | Verified and credible | Often unverified |

How to Become a Journalist?
- Obtain a degree in journalism or mass communication.
- Gain experience through internships.
- Develop strong research and writing skills.
The Future of Journalism
- AI-driven journalisms will become more common.
- Citizen journalisms will continue to grow.
- Ethical concerns around deepfake news will rise.
FAQs
Q2: Can journalism be completely unbiased?
While complete neutrality is difficult, ethical journalism strives for balanced reporting.
Q3: What impact does social media have on journalism?
Social media allows instant news dissemination but also contributes to misinformation.
Conclusion
Journalism remains the backbone of an informed society, ensuring transparency, accountability and democracy. While it faces numerous challenges, its role in shaping the world remains irreplaceable. With the right ethical framework, journalism will continue to thrive in the digital age.



Pingback: Arts