Introduction
The Roman Empire is one of the most remarkable civilizations in history, known for its vast contributions to art, architecture and culture. Roman arts encompass various forms of artistic expression, including sculpture, painting, mosaic work, frescoes and architecture. The Romans drew inspiration from Greek and Etruscan art, yet they developed a unique artistic style that reflected their society, politics and daily life. This article explores the different aspects of Roman arts in depth, including their history, significance, techniques and lasting influence.
The Evolution of Roman Arts
Early Influences and Development
The genesis of Roman art lies in its complex relationship with Etruscan and Greek artistic traditions. Initially, Roman artists drew heavily from these established styles, particularly embracing the naturalistic approach of Greek sculpture. However, as Rome’s power grew, its artists began developing their unique artistic voice, blending borrowed elements with distinctively Roman characteristics.
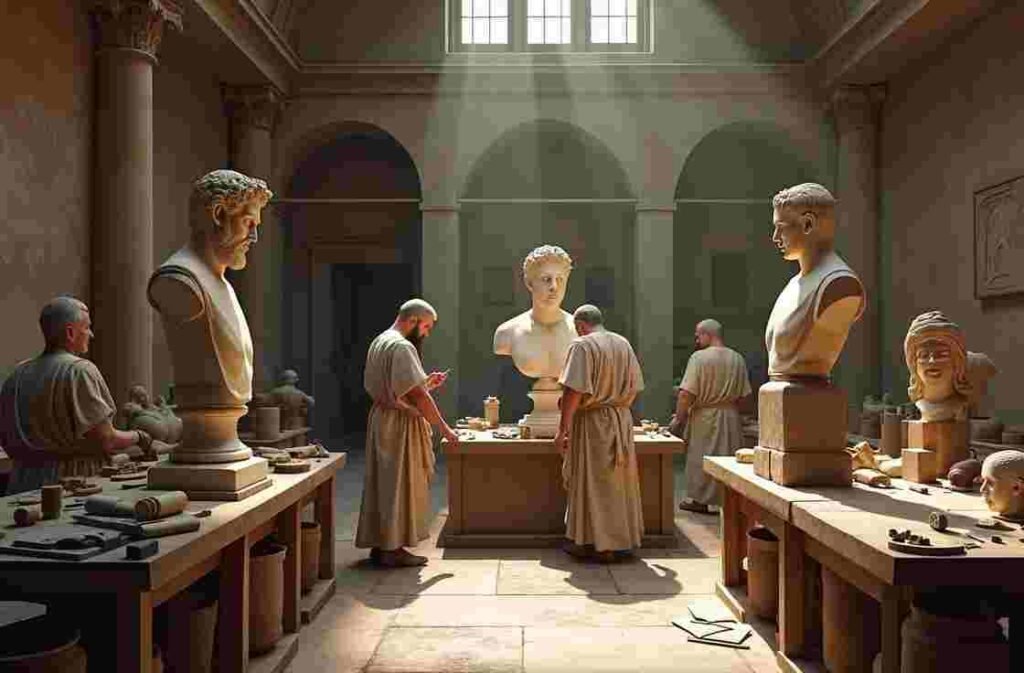
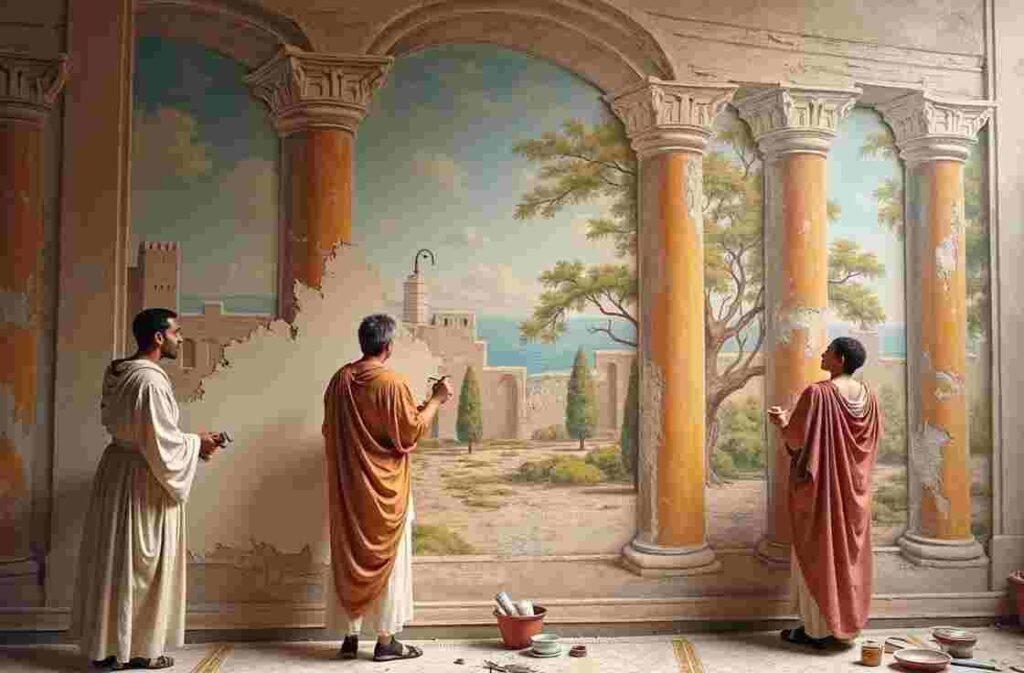


The Golden Age
During the Pax Romana (27 BCE – 180 CE), Roman art reached its zenith. This period witnessed unprecedented artistic innovation, characterized by:
- Masterful portraiture capturing realistic individual features
- Monumental architecture incorporating sophisticated engineering
- Revolutionary developments in wall painting and mosaic techniques
- Integration of art into daily life through decorative objects
Technical Innovations
Roman artists revolutionized several artistic techniques:
- Concrete Construction: The development of concrete allowed for unprecedented architectural achievements
- Glass Blowing: Romans perfected this technique, leading to mass production of glass vessels
- Fresco Painting: Advanced methods for wall painting, including the famous Pompeian styles
- Mosaic Techniques: Innovative use of tesserae to create detailed pictorial scenes
Major Forms of Roman Arts
Architecture
Roman architecture represents perhaps the most visible legacy of their artistic achievement. The Romans developed sophisticated engineering techniques that enabled them to construct massive structures that still stand today.
Key innovations include:
- The perfection of the arch and vault system
- Development of the dome as an architectural element
- Creation of the Composite order in column design
- Integration of practical engineering with aesthetic beauty
Origins of Roman Arts
Roman arts originated from a blend of influences, primarily Greek and Etruscan cultures. The Romans admired Greek artistry and incorporated many elements into their work, yet they infused their own cultural identity. The Etruscans, an ancient civilization in Italy, contributed significantly to Roman artistic development, particularly in funerary art and architectural techniques.
The early period of Ancient Roman Art can be classified into three major phases:
- The Monarchy Period (753–509 BCE): Characterized by Etruscan influences and rudimentary art.
- The Republican Period (509–27 BCE): Featured realistic portrait sculptures and early fresco paintings.
- The Imperial Period (27 BCE–476 CE): Marked the height of artistic achievement with grand sculptures, elaborate mosaics, and impressive architectural feats.
Key Characteristics of Roman Arts
Ancient Roman Art possess distinct characteristics that differentiate them from Greek and other ancient art forms:
- Realism and Individualism: Unlike the idealized forms of Greek art, Roman sculptures and paintings often portrayed realistic human features, including imperfections.
- Narrative and Propaganda: Many Roman artworks served political and historical purposes, depicting victories, emperors, and important events.
- Innovative Use of Materials: Romans employed materials such as marble, bronze, concrete, and stucco to create lasting artworks.
- Blend of Functionality and Aestheticism: Roman architecture and decorative arts combined beauty with practical use.
Roman Sculpture
Types of Roman Sculptures
sculpture of Roman can be categorized into several forms:
- Portrait Busts: Highly realistic representations of individuals, often used for commemorative purposes.
- Equestrian Statues: Monumental statues of emperors and military leaders on horseback.
- Relief Sculptures: Found on monuments and altars, these sculptures narrated historical events.
- Funerary Sculptures: Carved sarcophagi and tomb statues depicting the deceased.
Roman Painting and Frescoes
Roman paintings were often found in homes, public buildings, and religious temples. The four major styles of Roman frescoes, identified from the ruins of Pompeii, include:
- First Style (Incrustation Style): Painted to resemble marble.
- Second Style (Architectural Style): Created an illusion of three-dimensional space.
- Third Style (Ornate Style): Focused on delicate, decorative elements.
- Fourth Style (Intricate Style): A combination of all previous styles, with mythological and fantastical themes.
Mosaics in Roman Arts
Roman mosaics represent one of the most enduring art forms, featuring:
- Elaborate geometric patterns
- Narrative scenes from mythology
- Portraits and still lifes
- Functional floor decorations
Roman mosaics were intricate and vibrant, used to decorate floors, walls and ceilings. They often depicted mythological themes, daily life, and nature.
Roman Architecture and Its Influence
Roman architecture introduced several innovations, including the use of concrete, arches and domes. Famous structures include the Colosseum, the Pantheon, and aqueducts.
Decorative Roman Arts
Romans crafted exquisite jewelry, pottery and metalwork, often with intricate designs and motifs.
Technical Analysis: Materials and Methods
| Art Form | Primary Materials | Common Techniques | Typical Locations | Notable Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Stone, concrete, marble | Arch construction, vault building | Public spaces, private villas | Emphasis on engineering and durability |
| Sculpture | Marble, bronze | Lost-wax casting, direct carving | Forums, temples, homes | Realistic portraiture, narrative relief |
| Painting | Pigments, plaster | Fresco, encaustic | Villa walls, public buildings | Four distinct styles, vibrant colors |
| Mosaics | Stone, glass tesserae | Opus vermiculatum, opus sectile | Floors, walls | Detailed pictorial scenes, durability |
Materials and Techniques Used in Roman Arts
Romans used various materials, such as marble, bronze, wood and glass. They employed techniques like carving, fresco painting and mosaic assembly.
Famous Roman Artworks and Artists
- Augustus of Prima Porta
- Ara Pacis (Altar of Peace)
- Trajan’s Column
- Pompeii Frescoes
Legacy and Influence of Roman Arts
Roman artistic traditions influenced Renaissance art and continue to inspire modern architecture and design.
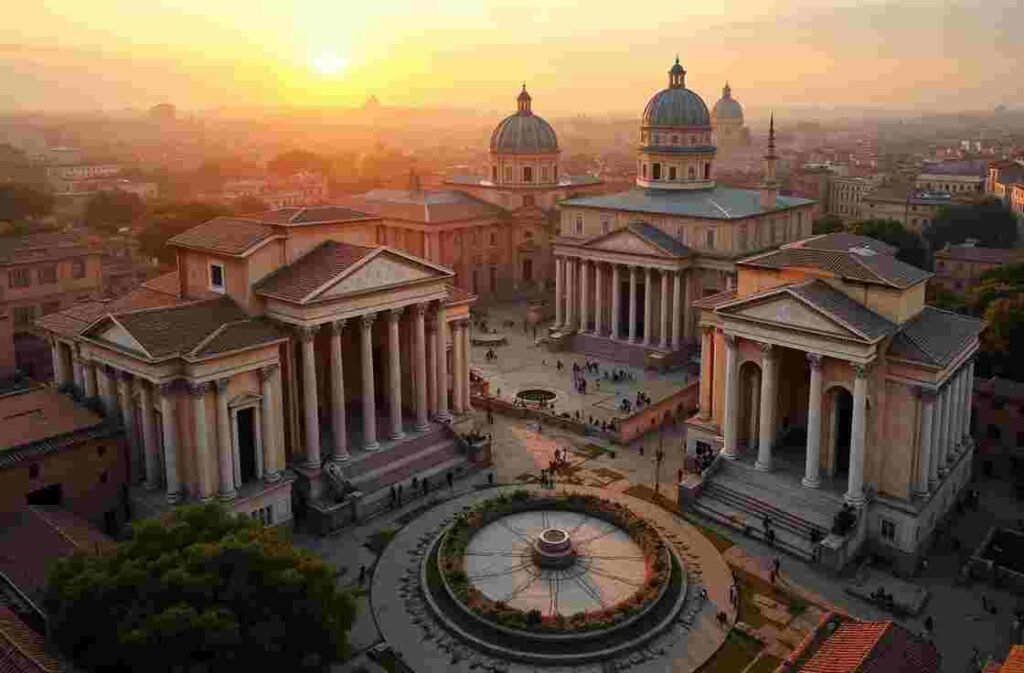
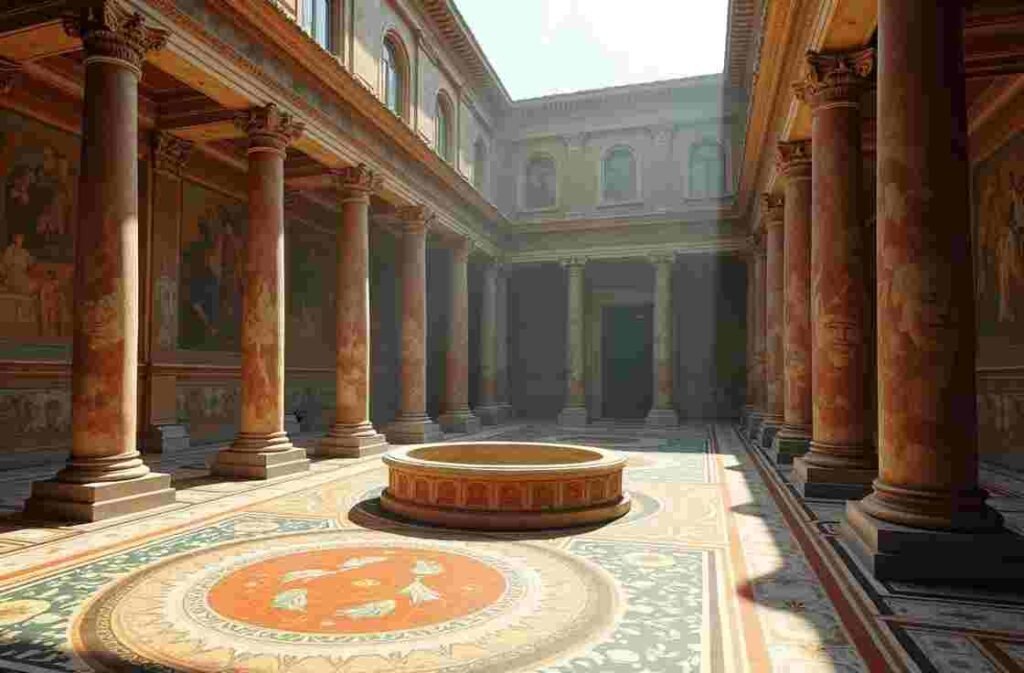


Cultural Impact and Legacy
Influence on Later Art
Ancient Roman Art has profoundly influenced Western artistic tradition through:
- Renaissance revival of classical forms
- Neoclassical architecture and sculpture
- Modern architectural principles
- Contemporary approaches to portraiture
Preservation and Conservation
The preservation of Ancient Roman Art has been crucial for understanding ancient civilization:
- Archaeological excavations revealing new discoveries
- Conservation techniques protecting existing works
- Digital documentation preserving information
- Museum collections sharing cultural heritage
FAQs on Roman Arts
Q: What materials did Roman artists use?
Roman artists worked with a wide range of materials including marble, bronze, glass, precious metals, and various pigments. They were particularly innovative in their use of concrete and development of new painting techniques.
Q: How did Roman art influence later periods?
Roman art profoundly influenced Medieval, Byzantine, and Renaissance art. Its impact can be seen in architecture, sculpture, painting techniques, and decorative arts throughout Western history.
Q: Were Roman sculptures really white?
No, Roman sculptures were originally painted in vibrant colors. Modern scientific analysis has revealed traces of pigments on many ancient sculptures, though the colors have faded over time.
Q: What is the most famous piece of Roman art?
While there are many contenders, the Augustus of Prima Porta, the Ara Pacis, and the frescoes of Pompeii are among the most celebrated examples of Roman art.
Q: How did Romans create their mosaics?
Roman mosaics were created using small pieces of colored stone or glass (tesserae) arranged to form patterns or pictures. Artists would follow preliminary sketches and use specialized tools to cut and place the tesserae.
Q: What role did art play in Roman society?
Art served multiple functions in Roman society, including religious devotion, political propaganda, historical documentation, and personal status display.
Q: How do we know what Roman art looked like?
Our knowledge comes from surviving artifacts, ancient literary descriptions, and particularly well-preserved sites like Pompeii and Herculaneum.
Q: Did Roman artists sign their works?
Unlike Greek artists, most Roman artists remained anonymous. Art was typically commissioned by patrons and considered more of a craft than a fine art.
Q: How did Roman art change over time?
Roman art evolved from early Etruscan influences through Greek-inspired Classical periods to more abstract late Imperial styles, reflecting changing tastes and social conditions.
Q: What are the main characteristics of Roman art?
Roman art is characterized by its realism, especially in portraiture, and its incorporation of various cultural influences, notably from Greece and Etruria. It encompasses a wide range of mediums, including sculpture, painting, mosaics, and architecture.
Q: How did Greek art influence Roman art?
Romans admired Greek art for its idealized forms and techniques. They often commissioned copies of Greek sculptures and incorporated Greek motifs into their own works, blending them with Roman elements to create a distinct style.
Q: What materials did Roman artists commonly use?
Roman artists utilized materials such as marble, bronze, terracotta, and fresco for sculptures and paintings. They also employed concrete extensively in architecture, enabling innovative structural designs.
Q: What role did art play in Roman society?
Art in Roman society served multiple purposes: it was a means of political propaganda, a display of wealth and status, a tool for religious expression, and a medium for preserving personal and historical narratives.
Q: How did Roman architecture differ from Greek architecture?
While Roman architecture borrowed elements from Greek designs, it introduced innovations like the arch, vault, and dome. Romans also made extensive use of concrete, allowing for more diverse and monumental structures.
Q: What are some famous examples of Roman art?
Notable examples include the Colosseum, the Pantheon, the Ara Pacis Augustae,
Conclusion
Roman art represents one of humanity’s most remarkable artistic achievements, combining technical innovation with aesthetic beauty. Its influence continues to resonate through the centuries, shaping our understanding of classical antiquity and informing contemporary artistic practice. The Romans’ ability to synthesize various artistic traditions while developing their own unique style demonstrates the power of cultural exchange and creative adaptation. Their legacy lives on not only in preserved artifacts but in the countless ways their artistic innovations continue to inspire and influence creators today.
Through their masterful integration of engineering and aesthetics, their development of new artistic techniques and their creation of enduring works of beauty, the Romans established an artistic tradition that remains vital and relevant in the modern world. As we continue to discover and study Roman artworks, our appreciation for their technical skill and creative vision only grows deeper.



Pingback: Indian Arts | A Comprehensive Guide to India's Cultural Heritage