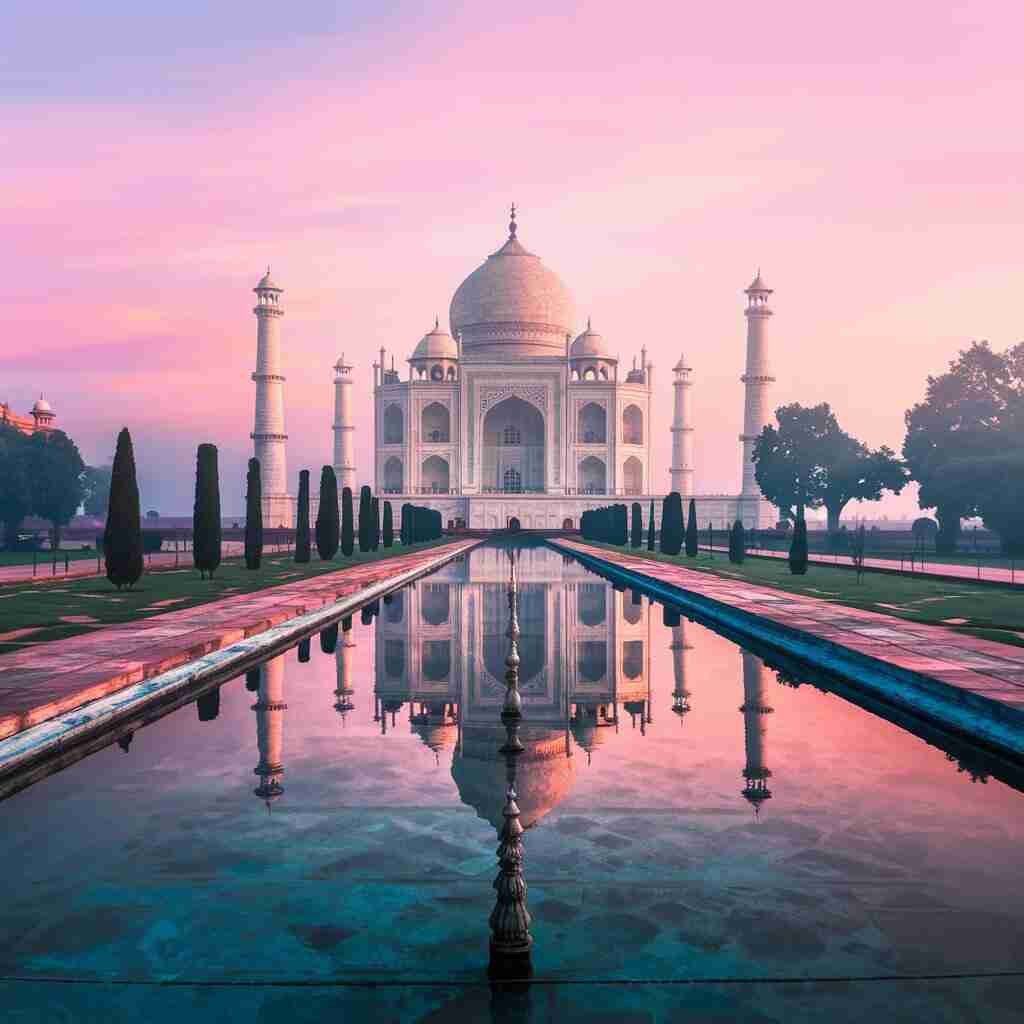
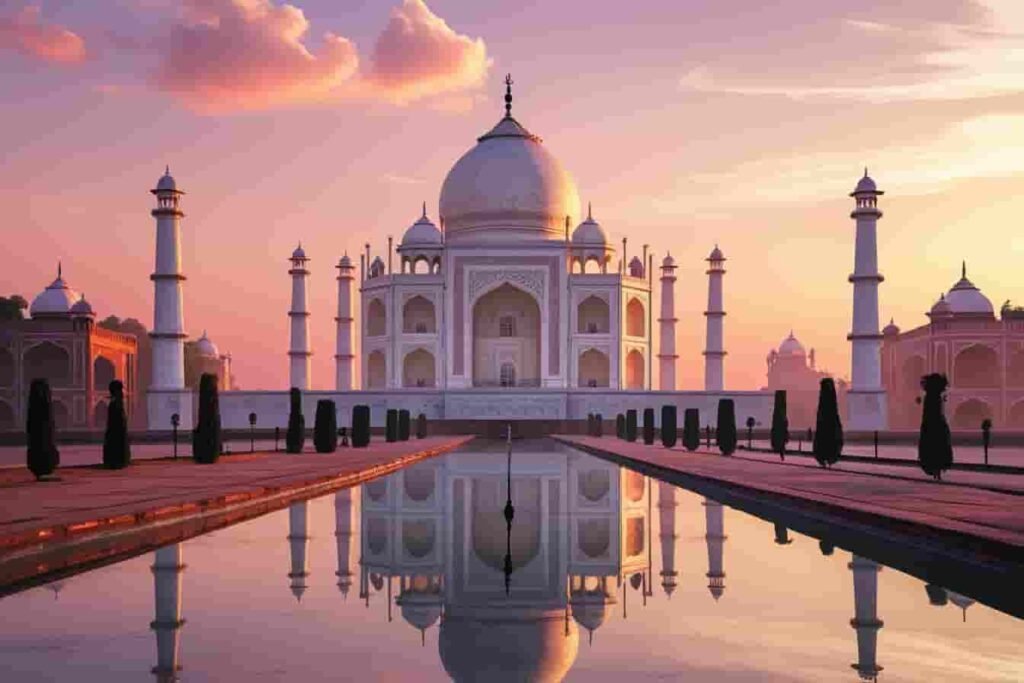
The Taj Mahal, often regarded as the pinnacle of Mughal architecture, is one of the most famous monuments in the world. Located in Agra India this breathtaking white marble mausoleum stands as a symbol of love built by Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his beloved wife Mumtaz Mahal.
With its impeccable symmetry intricate carvings, and ethereal beauty the Taj Mahal India continues to captivate millions of visitors each year. In this article we will explore every aspect of this iconic monument from its history and construction to its cultural significance and visitor experience.
Let’s embark on a journey to uncover the fascinating details behind the Taj Mahal an everlasting masterpiece that speaks of love art and heritage.

1. Introduction to the Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal India is an UNESCO World Heritage Site and is widely considered one of the most beautiful buildings in the world. Built between 1632 and 1648 this mausoleum is an architectural marvel that blends elements of Islamic Persian and Indian designs.
Standing on the banks of the Yamuna River, the Taj Mahal is surrounded by lush gardens water fountains and grand gateways adding to its majestic presence. It is a popular destination for tourists historians and photographers, who are drawn to its enchanting beauty and historical significance.
2. History and Origin
The Taj Mahal India was commissioned by Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in 1632 following the death of his favorite wife Mumtaz Mahal who died during childbirth. Deeply grieved by her loss he vowed to build a tomb that would be unparalleled in beauty.
The construction of the Taj Mahal took approximately 16 years, employing over 20,000 artisans engineers and laborers from across the empire. The finest materials were source from various parts of India and the world including
| Material | Origin |
|---|---|
| White Marble | Makrana, Rajasthan |
| Jasper | Punjab |
| Jade & Crystal | China |
| Lapis Lazuli | Afghanistan |
| Turquoise | Tibet |
| Sapphire | Sri Lanka |

3. Architectural Brilliance
The Taj Mahal is an example of Mughal architecture at its peak, characterized by symmetry intricate carvings and innovative engineering.
Main Architectural Features:
- Massive Dome: The central dome is 73 meters high giving it a grand, sky reaching appearance.
- Minarets: Four towering minarets surround the main structure slightly tilted outward to protect the main tomb in case of an earthquake.
- Calligraphy: Verses from the Quran are beautifully inscribed on the entrance arches.
- Reflecting Pool: The symmetrical design of the reflecting pool enhances the monument visual appeal.
The Taj Mahal India is a perfect blend of Persian Turkish and Indian architectural influences, making it one of the greatest human achievements in art and design.
4. Symbolism of the Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal is not just a tomb but a representation of eternal love purity and paradise. The entire structure symbolizes:
- Love and Devotion: Built as a tribute to Mumtaz Mahal.
- Heavenly Beauty: The use of pure white marble reflects purity.
- Islamic Paradise: Inspired by descriptions of Jannah (heaven) in Islamic tradition.
5. The Taj Mahal: A Wonder of the World
The Taj Mahal India was declared one of the New Seven Wonders of the World in 2007. This recognition further cemented its position as a global icon of architectural brilliance.
6. The Story of Shah Jahan and Mumtaz Mahal
Shah Jahan and Mumtaz Mahal’s love story is legendary. Mumtaz Mahal, the emperor’s favorite wife, died in 1631 while giving birth to their fourteenth child.This heart wrenching loss led to the creation of the Taj Mahal, which remains a symbol of love.
7. The Construction Process
The construction of the Taj Mahal India was a massive undertaking, involving:
- 20,000+ artisans
- 1,000 elephants for transportation of materials
- 16 years of craftsmanship
8. The Influence of Persian and Indian Architecture
The Taj Mahal reflects the best of Mughal, Persian, and Indian architecture, with influences seen in:
- Grand Persian-style gardens (Charbagh)
- Islamic calligraphy and geometric patterns
- Indian motifs and decorative elements
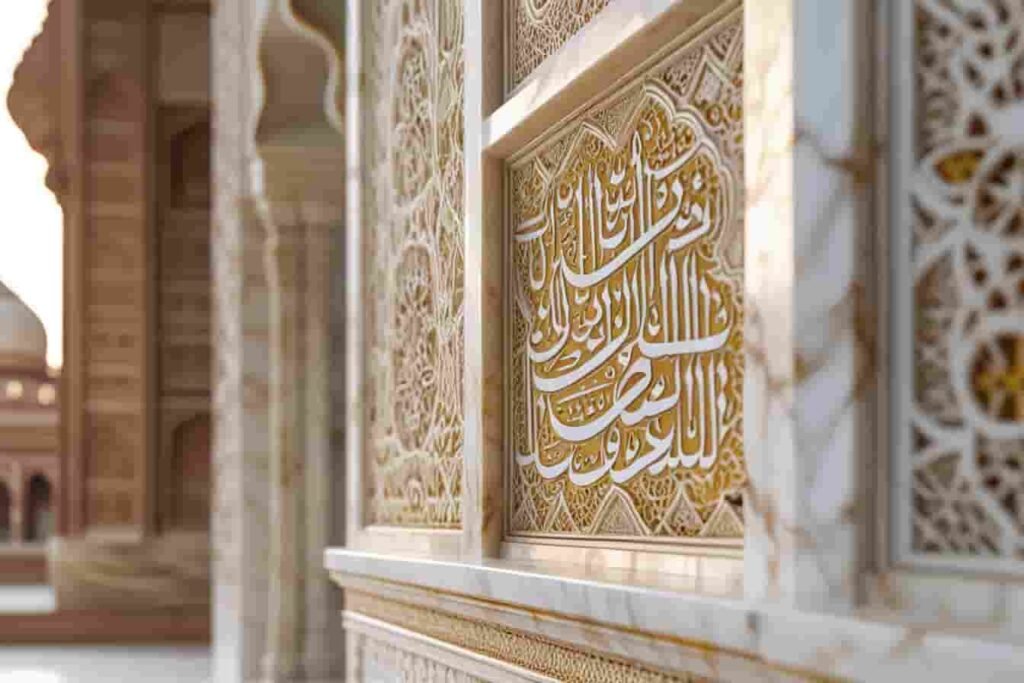

9. The Intricate Calligraphy and Decoration
One of the most mesmerizing aspects of the Taj Mahal India is its exquisite calligraphy, done by Amanat Khan. The walls are adorned with verses from the Quran, enhancing its spiritual significance.
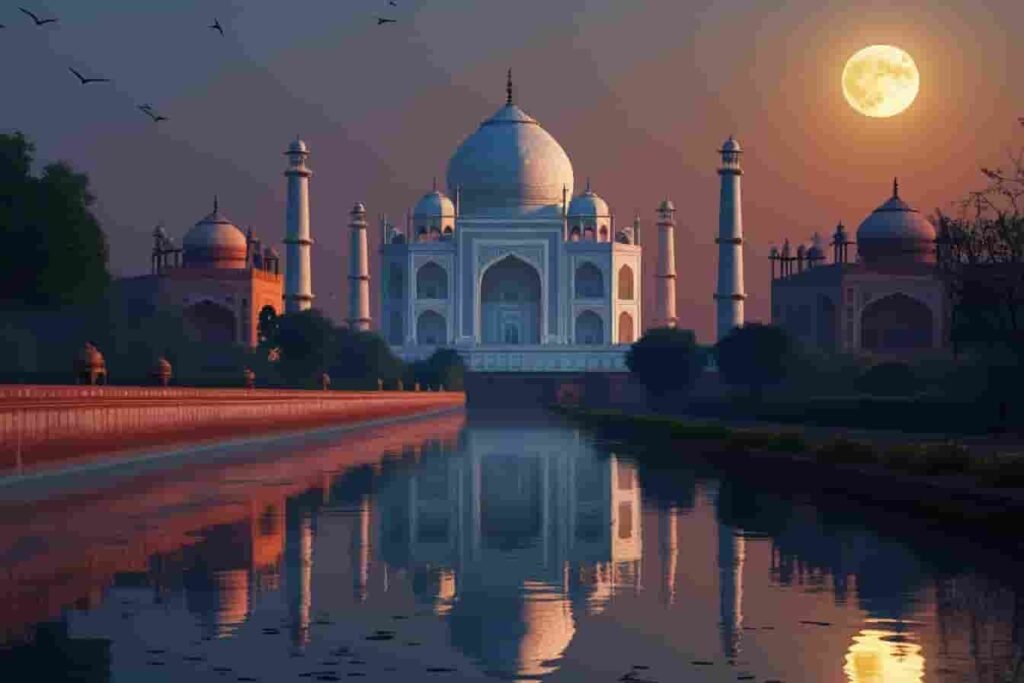
10. The Changing Colors of the Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal India appears to change color throughout the day:
- Morning: Soft pink hues
- Noon: Bright white glow
- Evening: Golden-orange shade
- Full Moon Night: Ethereal silver glow
FAQs
Q2. Can we visit the Taj Mahal at night?
Yes, night visits are allowed on full moon nights for a mesmerizing view.
Q3. Is the Taj Mahal India open every day?
The Taj Mahal is of on Fridays for prayer.
Q4. How long did it take to build the Taj Mahal?
It took approximately 16 years (1632–1648) to complete.
Conclusion
The Taj Mahal India is not just an architectural masterpiece but an eternal symbol of love, history, and craftsmanship. Its grandeur, artistic beauty, and deep emotional significance make it a must-visit destination.
If you haven’t visited the Taj Mahal, it should definitely be on your bucket list!